Amazon has had a transformative impact on consumer behavior, business practices, and market dynamics—a phenomenon often referred to as the “Amazon Effect.” At the core of this influence lies Amazon’s commitment to innovation in e-commerce, logistics, and customer service. By setting new standards for fast delivery, extensive product selection, and seamless shopping experiences, Amazon has fundamentally reshaped customer expectations and forced businesses across various industries to adapt quickly or risk falling behind.
Amazon has become a leader in this transformation largely due to its use of advanced warehouse robotics powered by cutting-edge software. These systems automate critical fulfillment tasks like order picking and sorting, reducing reliance on manual labor. This allows Amazon to process orders faster, with better inventory visibility and accuracy.
Robotic automation also helps Amazon handle dynamic challenges, such as shifting order priorities, adding new products, and fluctuating order volumes across distribution channels. As a result, they can meet ever-changing customer demands, especially during high-traffic shopping seasons like Black Friday and the holidays.
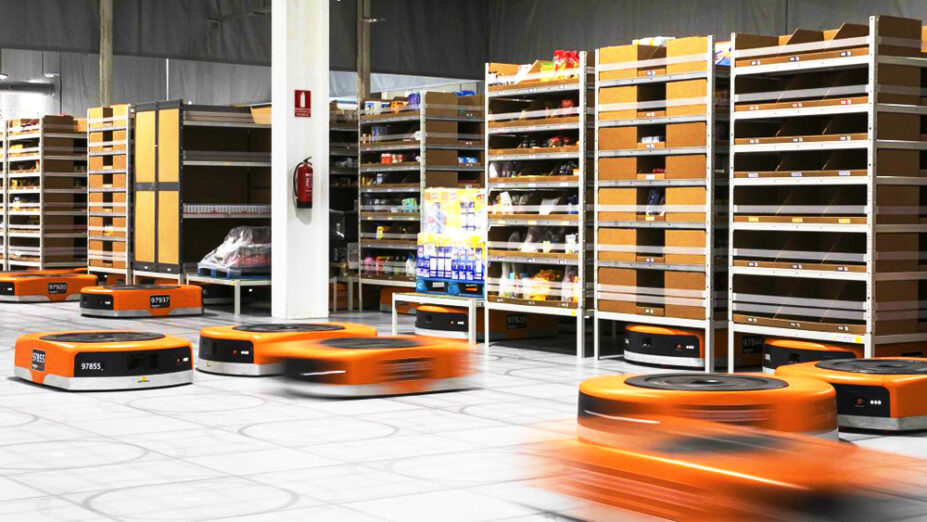

Amazon’s Kiva robots transport shelves stocked with goods throughout warehouses
The History and Growth of Amazon Robotics
Amazon’s journey into robotics began with its acquisition of Kiva Systems in 2012 for $775 million, marking a turning point in warehouse automation. Kiva robots, classified as Automated Mobile Robots (AMRs), were designed to zip across warehouse floors, transporting lightweight shelves with ordered goods to human operators for picking. This system significantly boosts efficiency by reducing manual picking time and improves order accuracy. It also creates a safer, more ergonomic work environment by minimizing the need for employees to bend and lift heavy items, or work near hazardous equipment like forklifts.
Since 2012, Amazon has introduced several robotic automation systems across its global warehouse network. These include enhanced versions of the Kiva system, such as Sequoia. Like Kiva, Sequoia uses mobile robots to transport shelves loaded with goods. However, it also incorporates automated picking stations that extract goods from the shelves and position them ergonomically for operators to pick, further streamlining operations and improving workplace ergonomics.
Amazon has also introduced various robotic arms to handle tasks like picking goods directly from bins, palletizing, and depalletizing. For example, Sparrow uses computer vision and AI to detect, select, handle, and sort individual items, placing them into bins for employees to prepare for final packaging.
The Ripple Effect of Amazon Robotics
The ripple effects of Amazon’s robotics-driven innovation extend beyond its fulfillment centers. Competitors have been compelled to adopt similar automation strategies to keep up, reshaping supply chain management and customer engagement strategies across the industry.
A key development has been the adoption of Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS), like the Exotec Skypod system, which uses mobile robots to move goods between storage racks reaching up to 39 feet tall and picking stations.
However, this trend toward robotics has also sparked important discussions about its impact on the labor market, including questions about whether robots will replace workers and how automation might reshape the future of work.

The Exotec Skypod system is an ASRS used by companies like Amazon to boost order fulfillment efficiency
Transforming Human Roles and Upskilling for Collaboration with Robots
Robots are best suited for handling the most tedious, time-consuming, and dangerous aspects of warehouse work. Manual picking and sorting have long been a significant part of this work, making it a key focus for Amazon and other companies investing in robotics.
It is not uncommon for pickers to walk more than 10 miles per day while picking goods within vast warehouses. The physical demands of the job make hiring and retaining workers challenging, resulting in staffing shortages and difficulties meeting the increasing demand for faster shipping and precise order accuracy—issues worsened by ongoing labor shortages. Automating these processes with robotics has enabled businesses like Amazon to ease workers’ physical strain and open opportunities for roles that require higher-level decision-making and problem-solving.
For example, Ariat, a leader in performance footwear and apparel, adopted the Skypod system. This helped them shift 80% of their picking labor to higher-value tasks while boosting their picking rate by 10 times. Some of the roles that robotics enables businesses to create for their employees include:
- Process Improvement: Robotics has enabled businesses to allocate more employees to developing and implementing strategies that streamline operations, reduce waste, and boost productivity.
- Data Management and Analysis: Automation generates vast amounts of data, which must be analyzed to optimize performance. New jobs have emerged in data analytics, improving operational efficiency and streamlining workflows.
- Technical Training: As companies embrace automation, the need for employees trained in robotics management and maintenance continues to grow.
- Order Customization: The demand for personalized goods and packaging tailored to specific customer orders or branding is steadily increasing.
- Quality Assurance and Control: Inspecting products for defects and ensuring compliance with customer and regulatory standards is essential for successful operations.
This shift in the labor market reflects how technology is changing the types of jobs available rather than eliminating them.
Where Amazon Robotics is Headed
Today, Amazon uses hundreds of thousands of robots across its global fulfillment network. Currently, robots are best suited for repetitive tasks, such as storing and retrieving goods, where their efficiency and consistency shine. While the hardware used by these robots is relatively simple, the real innovation lies in the software advancements that drive them. As advanced algorithms, AI, and the Internet of Things (IoT) continue to evolve, these systems will become capable of handling increasingly complex roles with precision and adaptability. The goal is to ensure that robots can take on complex tasks with a high degree of reliability.
In supply chain automation, reliability is crucial—especially in high-volume warehouses, where even a brief system shutdown can lead to major losses. A system outage of just a few hours can result in millions of dollars in losses due to employee overtime to catch up on orders, penalties for contract violations, expedited shipping costs, and canceled orders.
Looking ahead, Amazon’s robotics will likely integrate more deeply and reliably with artificial intelligence, machine learning, and autonomous systems that can adapt to changing fulfillment needs in real time, further enhancing fulfillment speed and operational efficiency to stay ahead in the logistics space.
Safety and Ergonomics Enhancements Enabled by Robotics
One key benefit of robotics is the improvement in workplace safety and ergonomics. In environments like Amazon’s fulfillment centers, repetitive tasks and lifting heavy items can lead to injuries over time. With robots handling the most physically demanding tasks, human workers face fewer risks of injury, resulting in a safer and healthier work environment.
Robotics has also reduced pedestrian traffic within the warehouse, minimizing the chances of collisions between workers and machines. This has further enhanced site safety, ensuring a more productive and secure environment for employees.

Economic Impacts: Productivity, Operational Costs, and Efficiency
The economic impact of robotics in fulfillment centers is substantial. They enable businesses to increase productivity while reducing operational costs. Robots can operate 24/7 without breaks, enabling faster order processing and higher throughput, which ultimately leads to higher rates of customer acquisition and loyalty.
As businesses like Amazon strive to position more facilities closer to customers in urban centers—where real estate costs are highest—robotic systems provide a significant edge. By enabling efficient use of space, robotics allow these companies to reduce costs by operating from smaller, strategically located facilities. Robots can operate in narrower aisles and access higher storage levels than human workers, effectively reducing the space required for storage.
Accurate order picking is another area where robotics helps businesses save costs. Order picking errors lead to lost future sales, expensive returns, and unsold inventory. Consider this: out of 1,000,000 orders, if the average order picking accuracy is 99%, it means that 10,000 orders could be wrong. That translates to 10,000 unhappy customers. This underscores the importance of order accuracy and the need for advanced automation to achieve it.
Robotics helps companies reduce their dependence on manual labor, reduce facility costs, speed up order fulfillment, and cut expenses from order errors. It’s an essential investment for businesses looking to thrive in today’s fast-paced market.
Future Outlook and Emerging Trends
As automation technology continues to evolve, the question of when will robots take over jobs is more about how quickly industries can adopt robotics solutions while balancing human labor. The future of robotics in fulfillment will likely see further advancements in software, enabling robots to take on more complex tasks beyond repetitive work.
As e-commerce expands and customer expectations rise, the demand for faster and more efficient fulfillment solutions will drive innovation in robotics. Robotics will continue evolving to meet customers’ specific needs and businesses growth.
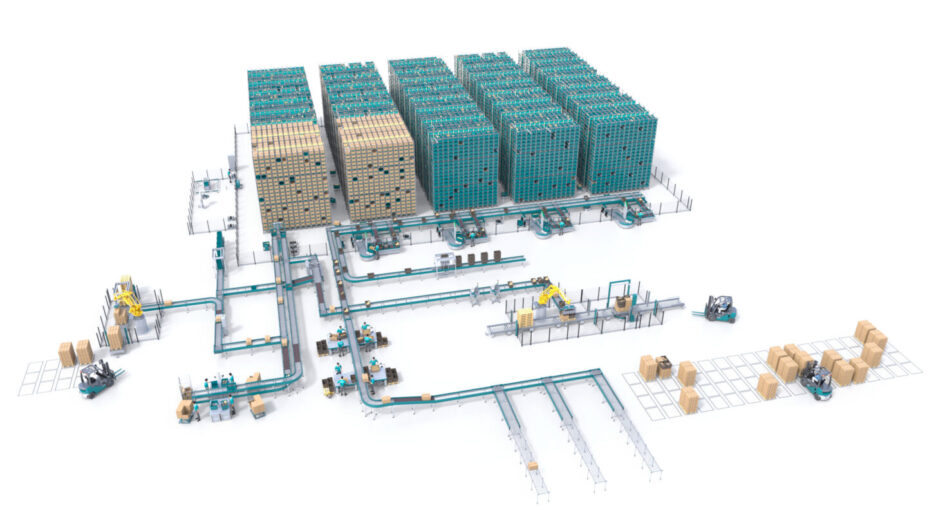
Our Approach to Automation at Exotec
When Amazon acquired Kiva Systems, it left a gap in the market for businesses seeking advanced robotics solutions. We at Exotec stepped in to fill that gap with our Skypod system, which uses elegant robotics to transport goods between high-density storage racks and ergonomic picking stations. What sets the Skypod system apart is its ability to maximize throughput and storage while delivering the flexibility to navigate an uncertain future.
The Skypod system can boost throughput performance by 5x compared to manual operations with the ability to retrieve any item in the system to a picking station within just two minutes. Its modular design enables businesses to independently scale throughput and storage. It can also process both cases and individual pieces for B2B and B2C orders within a single system.
To see how the Skypod system can transform your warehouse, we invite you to take our virtual tour and experience its capabilities firsthand.
Featured In
Share
Insights
-
April 15, 2025Top Warehouse Trends for 2025: Future of Automation
-
April 9, 2025Material Handling: Basics, Benefits, & Automation
-
April 4, 2025Complete Guide to Pick-and-Place Automation
News
-
March 24, 2025Exotec Showcases Next-Gen Skypod System at ProMat 2025
-
March 17, 2025Exotec Announces Partnership with Oxford Industries to Implement Next Generation Skypod System in New Multi-Brand Distribution Center
-
February 27, 2025Colruyt‘s Collect&Go continues its automation journey with Exotec
Events
-
May 7, 2025Exodinner: Indianapolis, IN
-
May 22, 2025 | Cincinnati, OHExotour: Cincinnati, OH
-
May 28, 2025Exodinner: Vancouver, BC